
Q: What, according to you, are the skill gaps persist in the automotive industry still and how is ASDC addressing this?
Sanghi: Automotive manufacturers are currently facing several challenges. With increased pressure to meet customer demand for more personalised designs, they are tasked with creating a more flexible production environment, reducing engineering time and costs, and accelerating the market to remain competitive.
With massive technological transformations taking place across the sector, companies need to keep pace with the ever-evolving landscape to meet the ever-evolving demands of modern-day work.
Acquiring new skills is the key to sustain in this dynamic landscape. It is a continuous effort of both the institute and the corporation to fill the skill gap. Although there are programmes, they are not reflecting the change at the same pace as the change seen by the industry.
Companies today need people who can adapt and develop themselves to the changing technology. Whether automotive or otherwise manufacturers have recognised the importance of creating a workforce of intelligent problem solvers. In addition to these, more manufacturers are now focusing on hiring and training talents that can sustain advances in technology and drive investment. We at ASDC are doing a lot of training activities along with our teams of various zones, including holding webinars and launching various courses.
We are also continually training our team members and associates and dealers to do more reviews on the digital platforms or dealers to focus on digital retail; they were not getting used to it.
They preferred to be physically present, talking face to face, but now this lockdown has left no other option but to adopt the digital route.
Q: Customers are well informed now, and they finalise the model and variant even before reaching the showroom. In this scenario, what kind of skills needed for dealerships?
Sanghi: With ever-increasing ways to capture your customers’ attention across multiple channels, a partner specialising in the customer journey can be an invaluable asset to your business.
Considering the experience from the consumer’s perspective allows the dealer to compete with other, less traditional models.
Social distancing will bring dynamic change to the dealership business. No longer will customers feel comfortable walking into showrooms. Now, the reverse will happen, and OEMs and dealers will have to reach out to customers even more. And going digital will help them do just that.
Sales channels, dealers and OEMs per se will have to increase the transparency level dramatically. That’s because customers will now prefer to engage with them virtually, which in turn means there has to be digital.
Various experiences, like test drives of new cars, which has been a very popular method of selling a passenger vehicle, will be a much-less-used tool for sales. Likewise, a physical inspection of vehicles undergoing maintenance will take a backseat, and the OEM/dealer will have to convey images to customers about the work being done, either in real-time or in some other manner.

Q: Would the new trend catalyse unemployment further?
Sanghi: The pandemic has brought forth the concept of work from home to enable social distancing, which earlier would never have been thought to be possible for a vast majority of the jobs. You will need to train them (workforce) on how to use digital tools, and train the entire ecosystem to monitor the efficiency.
The need for top-notch cybersecurity is vital; one has to be absolutely sure that the data is secured and not misused. Data integrity needs to be 100 percent. Organisations will need to upskill existing staff to be digital and tech-savvy. All the while, the focus has to be on the data which is supposed to be the oil of the economy that is secured and owned by the owner, and not someone else.
Q: How do you match the curriculum with the ever-evolving customer needs and changing regulatory environment?
Sanghi: While the automotive industry may be facing some challenges, digital manufacturing and technological progress are enabling automotive engineers to deliver products to market faster than ever before.
This is easing the competitive pressure on car manufacturers, and going some way to fill the void left by the shortage of skilled engineers.
COVID-19 has introduced digitalisation as the key to the future. For organisations and the country, this means a huge opportunity to upskill and reskill our workforce using digital tools. This will not only help the country stabilise manufacturing activities, but will also help to improve the standard of living, that well allows for economic growth.
Q: What are the challenges you face with emerging technology trends like electrified, automated, shared technology as each of these elements needs specialised training supported by adequate infrastructure?
Sanghi: A big change happening because of digitalisation and COVID-19 has just helped increase the focus. The current lockdown has brought the focus on skilling and digitalisation into sharp focus. Smart industrialisation is here to say; one can look at their people’s daily lives, particularly in urban and some parts of rural India, to experience that they are now more reliant on digital tools than they were in pre-COVID-19 days.
While skills shortage is an issue far wider than the automotive industry, reasons can be identified why this sector has a lack of skilled workers. For the manufacturing sector, it means moving from labour-intensive methodologies to automation. COVID has accelerated the growth of the cyber-physical world. India should marry men with the machine to enhance productivity. Highly skewed income distribution and a lack of respect for labour remain a big concern. Lack of respect leads to lower productivity and efficiency, which serve to robs India of a competitive edge.
Q: The technological changes that are coming off late are mostly the result of either legislation or regulation. In this scenario, how do you see ASDC transform in the future?
Sanghi: Demand-driven skilling has been the focus of every industry. At ASDC, we’ve conceptualised the digital platform in such a way that it provides all the information together, at one place. For example, the availability of jobs in a sub-sector, what is the prediction for upcoming job roles and what are the skills in demand. It will provide links to all our partners wherein they can share their projections and find the right candidates.
There have been many modifications to the apprenticeship programmes, and these are rightly intended in making it inclusive. We are happy with the Government making these phenomenal improvements, and we hope the industry members engage more apprentices. For the automotive sector, ASDC is the delivery partner for apprenticeships. We also see a lot of enthusiasm from component manufacturers and dealers to explore apprenticeship as an option to get a skilled workforce.
Q: Today, almost all vehicles, including trucks, are connected in one way or the other. What are the new challenges that emerge out of these connected vehicles? What is the solution from ASDC?
Sanghi: The automotive industry is converging with the information and communication technology (ICT) industry at a rapidly increasing rate. Technology is reshaping the global automotive sector. In the future, cars will become computers on wheels as tech players’ move into the automotive sector to leverage their existing capabilities.
When we are talking about the challenges, it can be the difference in lifecycles in the automotive and the mobile industry is a serious challenge for the future of connected cars. New features, such as operating system upgrades and new applications, are provided almost constantly for the smartphone, whereas car manufacturers work on five-year cycles. The advent of connected cars will dramatically change the dealership model as a whole. Salespeople must plan to spend an hour or more teaching customers how to use their car’s advanced technology.
Also, issues such as privacy, security, the cost of deploying a system, data ownership, driver distraction, and equity must be taken into consideration in the technology of connected vehicles/cars.
 Q: How is ASDC preparing itself to support the maintenance and repair of electric vehicles?
Q: How is ASDC preparing itself to support the maintenance and repair of electric vehicles?
Sanghi: Complex maintenance is one of the most common concerns that affect electric vehicle (EV) adoption. In reality, however, the intervals between each service in an EV are almost the same as for regular vehicles, and those services are usually less complicated. Traditional vehicles have hundreds of mechanical and moving parts, whereas an EV contains far fewer. Parts of an EV are generally easy to replace and don’t wear out as quickly.
The only major “potential” expense in EV maintenance is replacing the battery. As the vehicle reaches 100,000 miles, it may have lost up to 20% of its range.
Some batteries are designed to replace modules in contrast to the whole battery, but it depends on the way the car is made. Although it may take significantly less time to perform a service on an EV, there are other differences in the service process that can affect an OEM’s aftersales business.
We at ASDC have upgraded our training systems to look after the present modes of maintenance.
The way forward is our entire training programme is under review by industry partners. We have expert groups in R&D, manufacturing; they are in the process of reviewing all our occupational standards and upgrading them, not only for the present but also for the future.
Q: What is your view on data storing wirelessly that may affect multi-brand third-party service centres; how do you see ASDC playing a role in this?
Sanghi: Wireless connectivity for the vehicle may pose serious cybersecurity threats to a moving vehicle.
However, the issue of multi-brand third-party service centres, including service aggregator platforms, are here to stay.
ASDC in partnership with some of the industry partners is keen on providing Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) for existing manpower as well as upskilling training of existing workers through blended digital learning modules for new technologies linked to new norms like BS-VI standards of emission, etc.
Q: What is ASDC’s work on conserving resources like use of remanufactured parts?
Sanghi: All stakeholders, including the current Government, have felt the need for a well-balanced vehicle scrappage policy; we expect to see its roll-out soon. This can boost a lot in refurbished and remanufactured parts. It opens a new sub-domain, generating employment and entrepreneurship opportunities. Once the policy contours are known, the training qualifications and standards will be worked upon by ASDC.
Q: What are the new courses ASDC is planning to conduct in the near future?
Sanghi: ASDC has started work on new job roles in the areas of Industry 4.0 for manufacturing and maintenance areas and the entire domain of electric vehicles. We are modifying some of the existing job roles to update the new technological changes and disruptions that have taken place in this industry. (MT)
Kordsa Displays Next-Gen Composite Technologies At JEC World 2026
- By MT Bureau
- March 13, 2026

Kordsa, a subsidiary of Sabancı Holding, presented its advanced material technologies to a global audience at the JEC World 2026 trade show in Paris. The company featured its latest breakthroughs in composite technologies tailored for the aviation, energy and automotive sectors. The event also served as a platform for Kordsa to communicate its sustainable growth strategy and technological transformation to an international network of stakeholders.
Held from 10 to 12 March 2026, JEC World is recognised as the premier global event for the composites industry. By convening the entire value chain, the exhibition enabled Kordsa to prominently display its expanding role and expertise in composite materials. The company’s presence was reinforced by its international subsidiaries, including US-based Fabric Development, Inc., Textile Products, Inc. and Axiom Materials, Inc., alongside Italy’s Microtex Composites Srl., demonstrating a unified approach shaped by evolving market demands.
Among the key innovations showcased were Ceramic Matrix Composite (CMC) technologies, carbon-reinforced prepregs, thermoplastic automotive interior components and structural body parts. These solutions are engineered to deliver high performance and reduced weight while simultaneously boosting production efficiency and minimising carbon footprint. For the aviation and energy industries, the company highlighted advanced composites designed to meet stringent demands for high-temperature resistance, durability and operational reliability.
Ergun Hepvar, CEO, Kordsa, said, “JEC World is one of the most important global meeting points in the field of composite technologies. On this platform, which brings together the entire value chain of the industry, we have the opportunity to closely observe both the current state of technologies and the trends that will shape the future. This year, we clearly saw that solutions focused on sustainability, lightweighting, high performance and production efficiency are becoming increasingly decisive. At the same time, we witnessed a transformation in customer expectations towards more integrated, agile and sustainable solutions. As Kordsa, we will continue to be an active part of this transformation and to develop value-creating solutions together with our customers.”
Emphasising that Kordsa differentiates itself in composite technologies by offering an end-to-end integrated structure, from R&D and serial production to supply chain and certification processes, Hepvar further added, “The increasing demand for advanced material solutions further strengthens our position in composites. We position composite technologies as one of our two strategic focus areas in Kordsa’s future. In this field, we adopt an approach that expands technological depth, product diversity and application areas simultaneously. Composite technologies stand out as a core area shaping both Kordsa’s present and future. Our goal is to deepen our capabilities here, build a structure that generates higher added value, differentiates itself and grows together with its customers.”
- Kia UK
- 2026 Inspiring Automotive Woman of the Year
- 2026 Institute of the Motor Industry Awards
- 2026 IMI Awards
- Gender Equity
- Gemma Benbow
Kia UK’s Gemma Benbow Wins 2026 ‘Inspiring Automotive Woman of the Year’ Award
- By MT Bureau
- March 13, 2026

Gemma Benbow, People & Organisation Director at Kia UK, has been named the overall winner of the 2026 ‘Inspiring Automotive Woman of the Year’ award. The accolade was presented at the 2026 Institute of the Motor Industry (IMI) Awards, held in partnership with the Automotive 30% Club. Julia Muir, founder of the Automotive 30% Club, presented the award to Benbow.
The award celebrates women who drive meaningful change in the automotive sector, particularly in inclusion, talent development and workplace culture. Benbow was initially recognised as one of 24 winners of the ‘Inspiring Automotive Women Award’ during a private reception prior to the main IMI Awards dinner. She was then selected from this group as the overall recipient.

Judges commended her transformative leadership and strategic approach to diversity and inclusion, which have significantly reshaped internal practices at Kia UK. Benbow has embedded inclusive principles into recruitment, leadership development and overall workplace culture. Her influence also extends to external partners, where she has promoted cross-industry collaboration and helped strengthen inclusion efforts within Kia’s dealer network.
Through her advocacy for gender equity, Benbow has become a key role model, encouraging others to lead with empathy and bold thinking. Her work has bolstered Kia UK’s reputation as a leader in diversity and inclusion, and the company continues to celebrate her lasting impact in building a more representative automotive industry.

Julia Muir, Founder of the Automotive 30% Club and CEO of Gaia Innovation Ltd, said, “Gemma has made an incredible impact at Kia UK, where, as the first and only female director, she is not only driving change but also being the change. She is a transformative leader whose strategic vision and unwavering commitment to diversity and inclusion has reshaped the culture of the organisation. She exemplifies the spirit of this award and is a truly inspiring Automotive Woman.”
Nick Connor, CEO, IMI, said, “Gemma is a truly deserving recipient of this award. Her leadership, strategic vision and unwavering commitment to diversity and inclusion are helping to reshape the culture of the automotive industry and open the door for the next generation of talent. She is a powerful role model whose passion, empathy and determination to drive positive change perfectly reflect the spirit of this recognition.”
Benbow said, “I am incredibly honoured to receive the 2026 ‘Inspiring Automotive Woman of the Year’ award, and I’m truly grateful to both the Automotive 30% Club and the IMI for this recognition. It means a great deal to be acknowledged by such respected organisations within our sector.
“This award reflects the hard work Kia’s senior management and P&O teams have done to transform the culture of Kia UK, building an environment where inclusion, equity and a genuine sense of belonging are embedded into every part of the employee experience. I’m immensely proud of the progress we’ve made together and of the positive impact it has had both for our people and for the success of the business.
“I am proud to work for Kia, and I believe wholeheartedly that the company’s achievements are driven first and foremost by the talented, dedicated people behind it. This recognition is as much theirs as it is mine.”
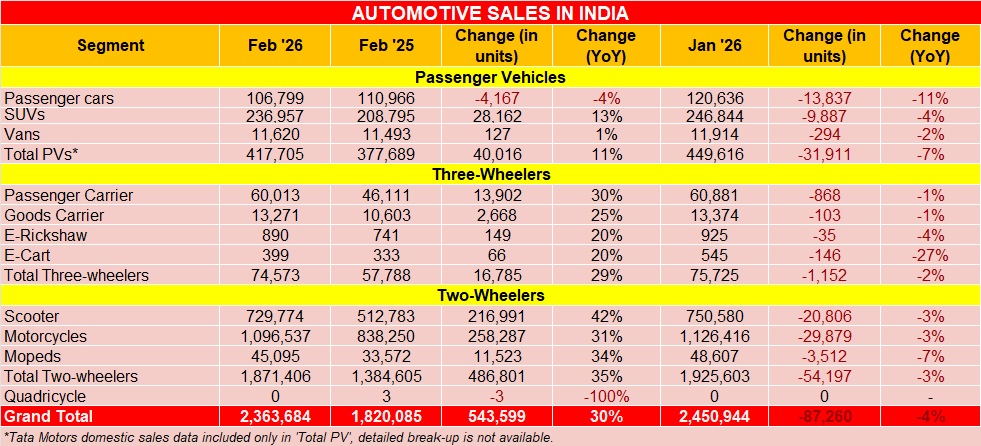
India Auto Wholesales Clock 30% Growth In February
- By Nilesh Wadhwa
- March 13, 2026

The automotive industry witnessed its best-ever sales for the month of February with a record 2.36 million vehicles sold across categories last month, which marks a 30 percent YoY growth as per the latest data shared by the Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM). For context, in February 2025, a total of 1.82 million vehicles were sold.
The two-wheeler segment reported a 35 percent YoY growth with sales of 1.87 million units, as compared to 1.38 million units last year. The performance was driven across categories – scooters (+42 percent), motorcycles (+31 percent) and mopeds (+34 percent).
The three-wheeler segment saw a 29 percent uptick with sales of 74,573 units, as against 57,788 units last year.
The passenger vehicle segment continued to witnessed a double-digit uptick with SUVs witnessing a robust demand. A total of 417,705 passenger vehicles were sold last month, as compared to 377,689 units a year ago. SUVs with 13 percent YoY growth continue to drive the momentum for the segment.
Rajesh Menon, Director General, SIAM, said, “Positive sentiments in the industry continues as passenger vehicles, two-wheelers and three-wheelers posted their highest ever Sales of February in 2026, with double-digit growth, compared to February 2025. While the month of March has festive drivers in several parts of the country, the recent conflict in West Asia remains a concern, both from the perspective of the supply chain, which could impact the manufacturing processes and exports. Industry would keep a close watch on evolving Geopolitical developments.”
Milan Nedeljkovic Elevated To BMW Board, Raymond Wittmann To Head Production
- By MT Bureau
- March 12, 2026

The Supervisory Board of German luxury brand BMW AG has appointed Raymond Wittmann to the Board of Management. He will assume responsibility for Production on 13 May 2026.
The appointment also coincides with Milan Nedeljkovic becoming Chairman of the Board of Management.
Wittmann joined the BMW Group in 2015 and has led Corporate Strategy and Corporate Development since 2024. His previous roles include Head of Assembly at the Munich plant, CFO of the Americas sales region, and Project Manager for the production site in San Luis Potosí, Mexico. He holds a PhD in aerospace engineering and previously worked as a partner at a consultancy.
Dr. Nicolas Peter, Chairman, Supervisory Board of BMW AG, said, “Raymond Wittmann combines strategic thinking with operational excellence and business responsibility. With his broad, cross-divisional experience and international perspective, he has the key qualities for leading the production division.”
“Raymond Wittmann complements the future Board of Management team led by Milan Nedeljkovic with the right strengths and skills. The Supervisory Board is very confident that the Board of Management, in its new composition, will continue to drive the success of the BMW Group in the future,” said Dr. Peter.






Comments (0)
ADD COMMENT